Background
Testosterone is one of the most universally well-known, but also commonly misunderstood hormones out there. It has captured the imagination of men since its discovery, entering popular imagination as a do-it-all hormone that’s universally responsible for “dude stuff.” Many people think that taking testosterone will be the cure-all to what ails them, and will turn every guy into a lean, trim, athletic, energetic horn-dog with the sexual prowess of an 18-year-old and the energy of a triathlete. We all wish that was true, but reality is a bit more complex. Here we’ll try to explore some of the details behind this popular hormone.
Understanding Testosterone
Testosterone is a hormone, primarily produced in the testicles, that has numerous effects on both male and female physiology (yes, women have a need for testosterone too!). It governs many well-known processes such as libido (sex drive), muscle mass, energy, mental alacrity – the list goes on. Having normal levels of testosterone, defined as roughly between 400-600, but up to 1000 or so in some men, is critical for normal emotional and sexual well-being.
What Causes Low T?
What causes a men’s testosterone to decline? For a long time we though it was aging, and although there is a mild gradual decline in T levels over time, there are very healthy men with T levels still rock solid well into their 70s. The real culprit is the accumulation of comorbid conditions. Basically, a healthy body makes good T levels, and an unhealthy body does not. Thus, the most common causes of low T are:
Just fixing these will go a long way to help return testosterone levels to normal.
400-600
Normal range levels of total testosterone in men. 1000 is necessary for some men.
10-15%
Body weight reduction can increase your testosterone by 150-200 points.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Being deficient in testosterone, a condition called male hypogonadism, can lead to all of these bad things listed below. In addition, emerging data shows that having prolonged hypogonadism can also increase the risk of diabetes, bone density loss, and even cardiac death. Thus, restoring men who are hypogonadal to the normal state can be a huge part of ensuring optimal health.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, testosterone could be a potential cause. The next step is to evaluate your hormone system with labs and then decide on a treatment plan, if appropriate.
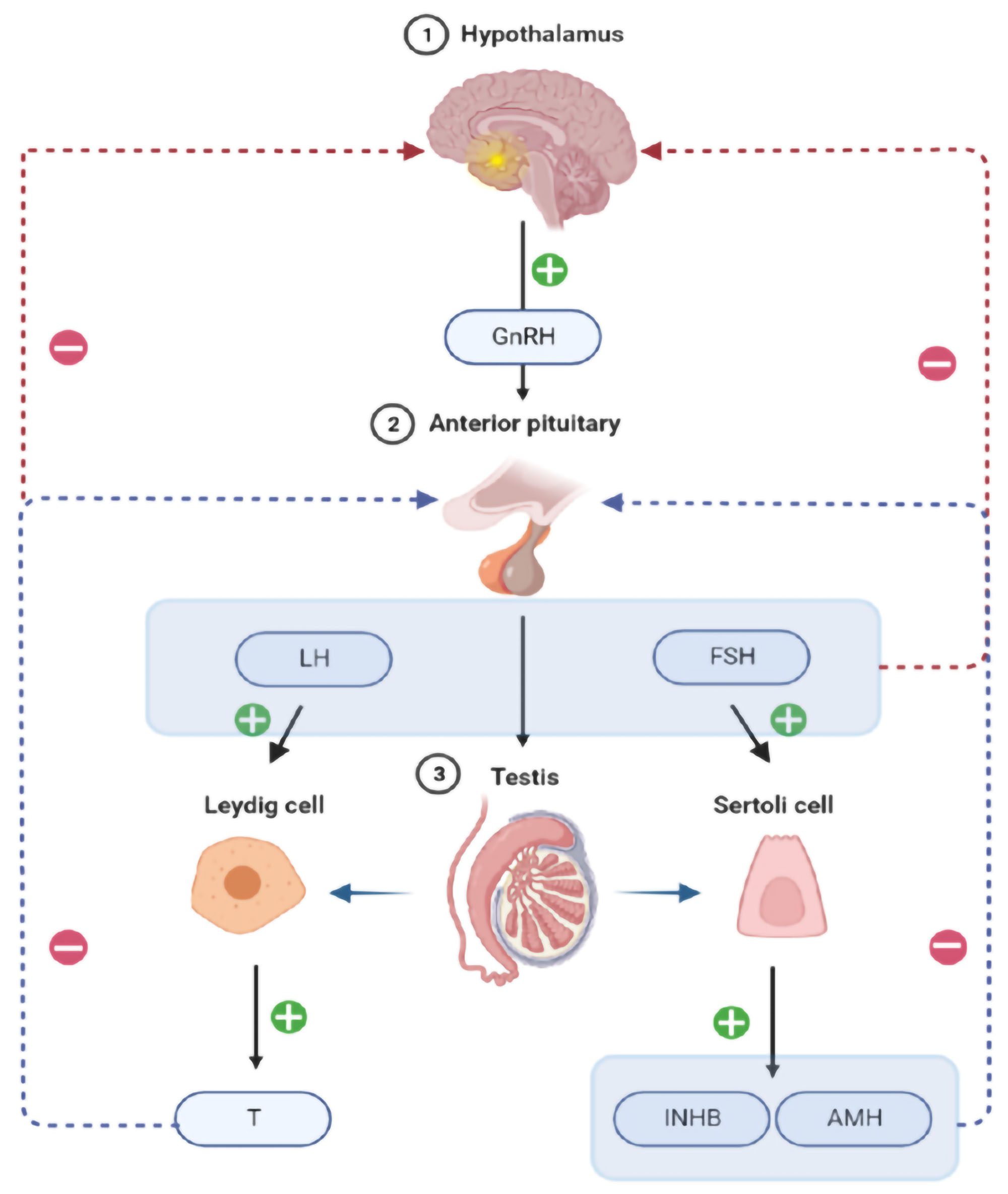
How Testosterone is Normally Made
The real long-term “win” for any Men’s Health advocate is to encourage men to make the lifestyle modifications needed to increase their own testosterone, enabling them to live happier, healthier, and more fulfilling lives. While the answer to increasing your testosterone can certainly be found in a bottle of testosterone cypionate, for most men, this will only ever be a compensatory solution, and does not get to the heart of the issue. The fundamental key to hormone health, and all health in general, is eating well, moving your body, and ensuring that you get good sleep. In patients with sleep apnea, getting on a mask can raise testosterone levels by 150-200 points alone! In obese men, losing 10-15% of your body weight can increase your testosterone by 100-150 points! These are the things we always start with, but for many men it’s not enough. That’s when we start using some pharmacological aids to get us there.

Treatment Options for Low Testosterone
Now that we understand the physiology, how do we increase testosterone levels? Here we break things down into two approaches. The first is the commonly known Testosterone Replacement Therapy, or TRT. This truly means replacing the body’s testosterone with external testosterone. The second approach doesn’t have a formal name, so let’s call it Internal Testosterone Boosting, or ITB for short. These two therapy paradigms have very different philosophies, so let’s explore them below.